Dijkstra's algorithm is an important topic in graph theory, where we can find the shortest path between two possible points in a graph. However, we can find the paths if they are having a cost > or = 0. This is an implementation of All pairs algorithm, where the cost is > or = 0.
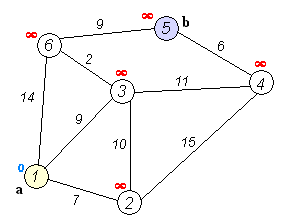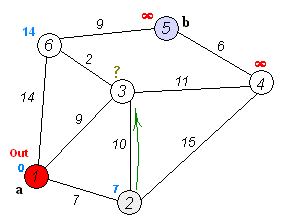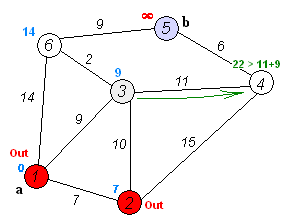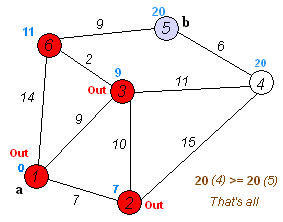 Fig. 1: A visualisation of Dijkstra's algorithm. Source : Wikipedia.
Fig. 1: A visualisation of Dijkstra's algorithm. Source : Wikipedia.
The main motive of this algorithm is to minimise the distance between two points in a map. Since this is a farely old algorithm, it is quite slow and takes a lot of space in the memory. There are several other algorithms that we can study, but this forms the basis of graph theory.
The basic algorithm is as follows, Note this is in layman's term:
INF <- A very large number Input the number of nodes as N Initialise an array A <- [N+1][N+1] to INF A[i][j] <- 0 where i = j for K = 1 to N do: for I = 1 to N do: for J = I+1 to N do: if A[K][J] > A[K][I] + A[I][J] A[K][J] = A[K][I] + A[I][J] A[J][K] = A[K][I] + A[I][J] endif endfor endfor endfor A <- Will contain the cost matrix A[source][dest] <- Will have the cost from source to destination
So let's start coding in GOD's language i.e., C++ :
Let's import the necessary libraires:
/*
* Floyd-Warshall - All pairs algorithm, written in CPP. Author: Jimut Bahan Pal.
* 4rth June, 2019.
*/
#include <iostream> // for input output
#include <bits/stdc++.h> // for templates, just in case
#include <iomanip> // for formatting and stuffs!
using namespace std; // for standard namespace, else use std:: for everything!
Now let's define the infinity. Here, it shall be a very big number which shouldn't be considered as an input.
#define INF 999999
We now can initialise the cost matrix, by taking the numbers as input. The N will the the total number of nodes as input. We have to initialise each element in the matrix to infinity. We then have to set the elements to 0 where i=j, after that we will print it, and here's how we will do it.
int main()
{
int N;
cin>>N;
int matrix[N+1][N+1];
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
matrix[i][j]=INF;
if(i==j)
matrix[i][j]=0;
}
cout<<"\n Initial cost matrix :=> \n\n";
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
cout<< setw(7)<< matrix[i][j];
}
cout<<"\n";
}
For a sample input of a graph which have 6 nodes and 7 verteces, with cost as shown, we will have to input like this:
Note: First line have the total number of verteces, second line have total number of connections and the third line
have each connections, starting node, ending node and the cost.
Then the initial cost matrix is displayed in the terminal like the following:
6 7 1 2 4 1 3 9 2 3 3 2 4 7 3 4 9 4 5 9 5 6 6 Initial cost matrix :=> 0 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 0 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 0 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 0 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 0 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 999999 0
Then we have to take the cost for each of the vertex that are available as link. We will then print the matrix for visualisation.
int T,i,j,cost;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>i>>j>>cost;
matrix[i][j]=cost;
matrix[j][i]=cost;
}
cout<<"\n Next cost matrix :=> \n\n";
//disp_matrix(matrix,N);
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
cout<< setw(6)<< matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
The output of this code segment in the terminal will be:
Next cost matrix :=>
0 4 9 999999 999999 999999
4 0 3 7 999999 999999
9 3 0 9 999999 999999
999999 7 9 0 9 999999
999999 999999 999999 9 0 6
999999 999999 999999 999999 6 0
Then we will perform the main part of the algorithm, where we will optimise the cost by brute force.
for(int k=1;k<=N;k++)
{
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<=N;j++)
{
if(matrix[k][j]>matrix[k][i]+matrix[i][j])
{
matrix[k][j]=matrix[k][i]+matrix[i][j];
matrix[j][k]=matrix[k][i]+matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
}
Hence, the matrix is optimised, and we print the matrix.
cout<<"\n Final cost matrix :=> \n\n";
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
cout<< setw(6)<< i<<" ";
}
cout<< endl;
cout<< setw(6)<<"-------";
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
cout<< setw(6) <<"-------";
}
cout<< endl;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
cout<< i<<"|";
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++)
{
cout<< setw(6)<< matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
The final output of the cost matrix generated upon optimisation via djiktras algorithm will be something like:
Final cost matrix :=>
1 2 3 4 5 6
-------------------------------------------------
1| 0 4 7 11 20 26
2| 4 0 3 7 16 22
3| 7 3 0 9 18 24
4| 11 7 9 0 9 15
5| 20 16 18 9 0 6
6| 26 22 24 15 6 0
So we have sucessfully implemented out Dijkstra's algorithm using GOD's language. Next, we will see how to solve the same problem in a different algorithm which is quite optimised in terms of space and time complexity!
Till then.... Happy coding!